
In the digital age, where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the online world, understanding web security threats is crucial to safeguarding our personal information and digital assets. From phishing attacks to malicious scripting, there are various techniques that cybercriminals employ to exploit vulnerabilities in web browsers and compromise user data. Let's delve into some of the most common web security threats:
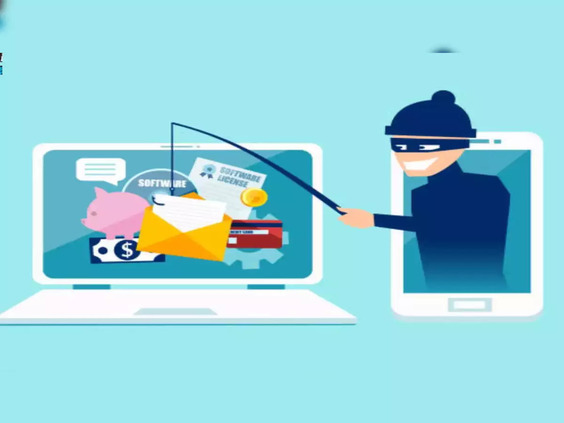
Phishing (Spoofing): Phishing attacks involve the use of deceptive tactics to trick users into divulging personal information such as login credentials, credit card details, or other sensitive data. Spoofing techniques, such as faking browser interface elements like the address bar or padlock, are often used to create convincing phishing websites.
Eavesdropping: Eavesdropping, also known as passive listening, involves unauthorized interception of browsing activity. Attackers may secretly monitor communication between a user and a website, potentially compromising sensitive information exchanged during the session.
Man-in-the-Middle Attack (MITM): In a MITM attack, an attacker intercepts and modifies messages exchanged between two parties without their knowledge. This allows the attacker to read, insert, or alter data transmitted between the user and the website, posing a significant threat to data confidentiality and integrity.
Spyware: Spyware refers to malicious software installed on a user's computer without their consent. It can intercept user interactions, collect personal information, and even modify browser behavior. Spyware programs can compromise user privacy and security, leading to unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Malicious Scripting: Some websites may contain malicious scripts or active content designed to deceive users or exploit vulnerabilities in web browsers. These scripts can trick users into providing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise their security.
Java, Active Content, and Plug-ins: Java, JavaScript, VBScript, and other scripting languages are commonly used to develop active content for websites. While these technologies enhance website functionality, they can also introduce security risks if not properly implemented or secured.
Cookies: Cookies are small text files stored on a user's computer by websites to store user-specific information. While cookies serve legitimate purposes such as session management, they can also be exploited by attackers to track user activities or steal sensitive data stored within them.
Security Zones and the Domain Model: Security Zones and the Domain Model are security features designed to provide multiple levels of security settings for web browsers. These features help mitigate risks associated with browsing untrusted websites and enforce security policies to protect user data.
In conclusion, staying informed about web security threats and implementing best practices for safe browsing are essential to safeguarding personal information and preventing cyberattacks. By understanding the techniques used by cybercriminals and adopting proactive security measures, users can minimize the risk of falling victim to online threats.
- CyberAwareness CyberSafety
You May Also Like It
In today’s fast-paced digital world, online scams have evolved into
In today's digital age, Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are
Leave A Comment
Don’t worry ! your e-mail address will not published.








0 Comments